In financial markets, numbers alone rarely tell the full story. Beyond fundamentals, charts, and economic data, market sentiment, the collective mood or psychology of traders, plays a massive role in both short- and long-term price movements.
How sentiment shapes trends can help traders make more informed decisions, reduce risk, and spot opportunities that purely technical or fundamental approaches might miss.
What Market Sentiment Really Means
Market sentiment is essentially the overall feeling or bias that traders have about an asset’s future price movement. In the short term, it’s often driven by emotions like fear and greed, news events, or even social media trends. In the long term, sentiment aligns with structural factors.
Even when fundamentals suggest one direction, a strong collective mood can push prices in the opposite direction.
Sentiment in the Short Term: Fast and Volatile
Short-term price movements are highly sensitive to sentiment. Traders reacting to headlines, tweets, or real-time data can cause rapid price swings. Algorithmic trading systems now routinely incorporate sentiment analysis to capture these movements, scanning news, and social signals.
For example:
- Sudden bullish sentiment can trigger breakouts, even before any formal news confirms the move.
- Negative sentiment can amplify selling pressure and trigger volatility spikes, often temporarily overshooting the “true” price.
These dynamics show why short-term traders need real-time tools and indicators that track sentiment alongside traditional technical analysis.
Measuring Market Sentiment: The Technical Side
Modern finance no longer relies solely on gut feelings. Sentiment can be quantified and modeled using computational tools:
- Algorithmic sentiment indicators: AI-powered systems scan market data, news, and social signals to produce sentiment scores that correlate with price movements.
- Time-series models, such as VAR or TVP-SV frameworks, can simulate how sentiment affects volatility and directional trends over time.
- Integrated systems: Traders often combine sentiment scores with classic technical indicators such as moving averages, RSI, and support/resistance levels to enhance precision.
These tools allow traders to act on sentiment signals without getting lost in the noise of emotional decision-making.
Market Patterns and Sentiment: A Symbiotic Relationship
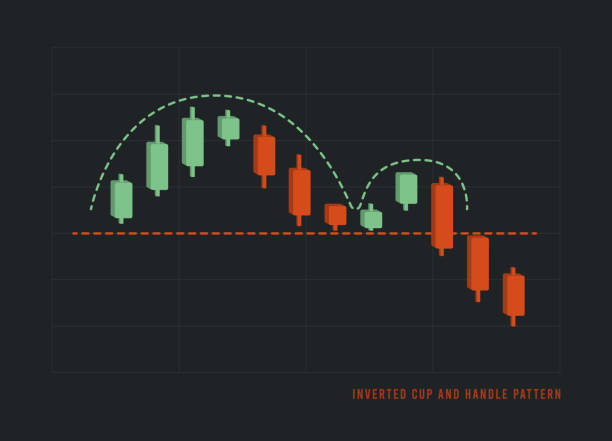
Interestingly, market sentiment often manifests in price patterns. For instance, consolidation phases, breakouts, and trend reversals often mirror shifts in trader psychology. One technical structure particularly tied to sentiment is the cup-and-handle pattern.
- The “cup” forms during a period of uncertainty or neutral sentiment, as prices dip and then gradually recover.
- The “handle” emerges when short-term sentiment hesitates, often before a breakout driven by renewed optimism.
Patterns like these show that price structures aren’t arbitrary; they’re expressions of collective sentiment, crystallized into recognizable shapes.
Practical Applications for Traders
So, how can traders leverage sentiment knowledge effectively?
- Short-Term Trading: Use real-time sentiment indicators to time entries and exits. A sudden spike in positive sentiment may justify taking a position even before fundamental news arrives.
- Long-Term Investing: Track sentiment trends to filter noise and validate whether a longer-term trend is supported by sustained trader behavior.
- Technical Confirmation: Combine sentiment insights with chart patterns to confirm potential breakouts or reversals.
The Takeaway
Ultimately, combining quantitative sentiment metrics, technical patterns, and informed judgment creates a robust framework for navigating both the rapid swings of day trading and the strategic horizons of long-term investing.

Leave a Reply