In today’s digital world, financial institutions and online platforms must ensure that their users are who they claim to be. This is where KYC comes into play. The term is widely used in banking, fintech, crypto, and many other industries, but not everyone clearly understands its purpose and value.
This article explains the KYC meaning, how kyc verification works, and why technologies like biometric checks are becoming essential.
What Is KYC? (KYC Meaning Explained)
What is KYC?
KYC stands for Know Your Customer. It is a set of processes used by businesses to verify the identity of their clients before establishing a professional relationship.
The main goal of KYC is to prevent illegal activities such as fraud, money laundering, terrorist financing, and identity theft. By understanding who their customers are, companies can operate in a safer and more compliant environment.
In simple terms, the KYC meaning refers to knowing, verifying, and continuously monitoring customers.
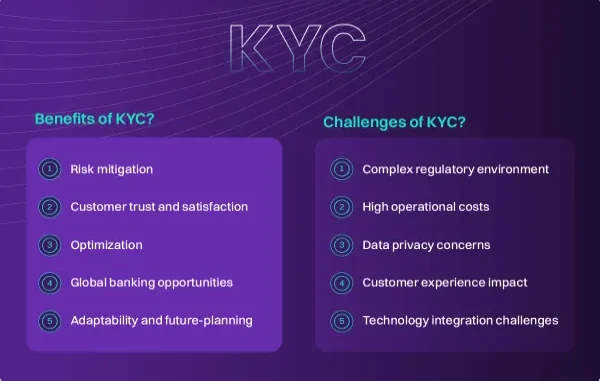
Why KYC Is Important for Businesses
KYC is not just a regulatory requirement — it is a critical risk management tool.
Key reasons why KYC is essential:
- Prevents financial fraud and identity theft
- Helps detect and stop money laundering
- Ensures compliance with local and international regulations
- Builds trust between companies and customers
- Protects platforms from legal and reputational risks
Without proper KYC procedures, businesses may face heavy fines, license revocation, or loss of customer confidence.
How KYC Verification Works
KYC verification usually involves several stages designed to confirm a user’s identity and assess potential risks.
Typical KYC verification steps include:
- Customer identification
- Collecting personal data such as full name, date of birth, and address
- Document verification
- Uploading official documents (passport, ID card, driver’s license)
- Identity authentication
- Confirming that the user is the real owner of the documents
- Ongoing monitoring
- Reviewing transactions and behavior over time
These steps help ensure that the user is legitimate and not involved in suspicious activities.
What Is Biometric Verification in KYC?
What Is Biometric Verification?
What is biometric verification?
It is a method of identity verification that uses unique biological characteristics to confirm a person’s identity.
Biometric verification has become a key component of modern KYC systems due to its accuracy and convenience.
Common biometric methods used in KYC:
- Facial recognition
- Fingerprint scanning
- Voice recognition
- Iris or retina scanning
By combining biometric data with document checks, companies significantly reduce the risk of impersonation and fake identities.
Industries That Rely on KYC
KYC is used across many sectors, especially those dealing with money and sensitive data.
Industries where KYC is mandatory:
- Banks and financial institutions
- Cryptocurrency exchanges
- Payment service providers
- Online lending platforms
- Insurance companies
As regulations continue to evolve, even non-financial platforms are increasingly adopting KYC procedures.
The Future of KYC
KYC is rapidly evolving with the help of artificial intelligence and automation. Modern kyc verification solutions aim to balance strong security with a smooth user experience.
Key trends in KYC development:
- Increased use of biometric verification
- Faster digital onboarding
- AI-powered fraud detection
- Global standardization of KYC rules
As digital services expand, KYC will remain a cornerstone of secure and trustworthy online interactions.
Conclusion
Understanding what is KYC and how it works is essential in the modern digital economy. From verifying identities to preventing financial crime, KYC protects both businesses and customers. With advancements such as biometric technologies, KYC processes are becoming more secure, efficient, and user-friendly.
In a world where trust is critical, KYC is no longer optional — it is a necessity.

Leave a Reply