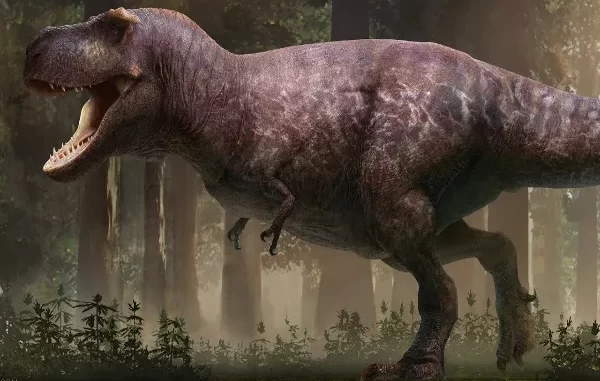
Tyrannosaurus Rex, often referred to as T-Rex, is one of the most iconic and powerful dinosaurs to ever roam the Earth. With its massive size and ferocious bite, T-Rex has become a symbol of prehistory and the apex predator of its time.
Scientists have studied T-Rex for years, uncovering facts and stats about its anatomy, lifestyle, and behavior. Though the information is limited due to the fact that T-Rex has been extinct for over 65 million years, paleontologists have uncovered an incredible amount of data about this giant creature. This article will provide an introduction to T-Rex’s life, including facts, stats, and a brief bio.
The Anatomy of Tyrannosaurus Rex: Exploring the King of the Dinosaurs
The Tyrannosaurus rex is a species of dinosaur that has captivated the imagination of many with its immense size and powerful features. As one of the most famous dinosaurs known to man, it is essential to have an understanding of its anatomy so that we can better understand the creature that once roamed the Earth.
The Tyrannosaurus rex was a bipedal carnivore that stood approximately 12 to 13 feet tall and measured up to 40 feet in length. It had a robustly-built body, a large head, and short but powerful arms. Its skull was 5 feet long, and its jaws were lined with over 50 sharp teeth. Its back was made up of four vertebrae that were supported by robust leg bones.
Its tail was approximately 4 feet long and served as a counterbalance to its massive body. The Tyrannosaurus rex was an incredibly powerful creature, and it had several adaptations that allowed it to be a successful predator. It had large olfactory bulbs, which allowed it to have an excellent sense of smell, enabling it to detect potential prey from a great distance.
Its eyes were forward-facing, providing it with excellent binocular vision. Its forelimbs were strong and included two fingers, which it used to grab and hold its prey. The Tyrannosaurus rex was an impressive species, and its anatomy was essential to its success. Its large size, powerful features, and remarkable adaptations allowed it to survive and thrive in the prehistoric world.
Its anatomy is still studied today, providing us with an incredible insight into the King of the Dinosaurs.
Tyrannosaurus Rex: The Most Fearsome Predator of the Cretaceous Period
Tyrannosaurus Rex (T. Rex) was one of the most fearsome predators of the Cretaceous period. This giant carnivore, which lived approximately 66 to 68 million years ago, was the largest land-based predator of its time, measuring up to 40 feet in length and weighing up to 10 tons.
T. Rex was a bipedal dinosaur, meaning it walked on two legs rather than four. It had a large skull with powerful jaws and large, sharp teeth which were designed for tearing and crunching through flesh. Its eyes were set on the sides of its head, allowing it to have a wider range of vision than its prey. Its tail was long and flexible, providing it with balance and agility.
T. Rex had short, but strong forelimbs, equipped with three fingers and claws. These were used for grasping and manipulating food, as well as for gripping and holding onto prey. Its hind legs were much longer and stronger than its forelimbs, enabling it to run at speeds of up to 20 to 25 miles per hour.
T. Rex was an apex predator and hunted a wide range of prey, including hadrosaurs, ceratopsians, ankylosaurs, and pachycephalosaurs. It was also known to scavenge dead animals. Its size and strength made it virtually unstoppable and its powerful jaws could crush bones with ease. T. Rex was a dominant predator of its age and its presence helped shape the ecology of the Cretaceous period. Its extinction marked the end of an era and the beginning of a new one.
While its reign of terror is now over, it will forever be remembered as one of the most fearsome predators of all time.
Uncovering the Evolutionary History of Tyrannosaurus Rex: A Closer Look at Its Ancestors and Descendants
The Tyrannosaurus Rex is one of the most iconic dinosaurs of all time. It has long been a source of fascination for scientists and laypeople alike, and its evolutionary history is no less intriguing. In this article, we will take a closer look at the evolutionary history of the Tyrannosaurus Rex, exploring its ancestors and descendants in greater detail.
The family tree of the Tyrannosaurus Rex can be traced back to the Late Jurassic period, approximately 150 million years ago. At this time, there were several different species of large theropod dinosaurs, including Allosaurus, Ceratosaurus, and Stegosaurus. It is believed that the T. Rex is descended from one of these species, though which one is still a matter of debate.
The earliest known ancestor of the T. Rex is called Proceratosaurus. This species lived during the Middle Jurassic period and was a small, carnivorous dinosaur. It was about three feet long and weighed about 20 pounds. It had a long, narrow skull with a pair of horns above the eyes and a short, thick tail. This species is thought to have been a scavenger, feeding on small animals and carrion.
The next ancestor of the T. Rex is called Dilophosaurus. This species also lived during the Middle Jurassic period and was a large, predatory dinosaur. It was about twenty feet long and weighed about two tons. It had a long neck, an elongated skull, and a pair of crests on its head. This species is thought to have been a top predator, hunting other dinosaurs and feeding on large prey. The closest relative of the T. Rex is called Tyrannosaurus Rex.
This species lived during the Late Cretaceous period and was the largest of all the predatory dinosaurs. It was about forty feet long and weighed about seven tons. It had a huge skull with powerful jaws and sharp teeth, and its tail was highly flexible. This species was a formidable predator, capable of taking down even the largest of prey.
The descendants of the T. Rex are called coelurosaurs, which include birds and various small, feathered dinosaurs. These species evolved from the T. Rex during the Late Cretaceous period and continued to diversify and spread across the globe. Today, many species of birds are believed to be direct descendants of the T. Rex.
In conclusion, the evolutionary history of the T. Rex is complex and fascinating. It can be traced back to the Late Jurassic period and its closest relatives include Proceratosaurus, Dilophosaurus, and other large theropod dinosaurs. Its descendants are the coelurosaurs, which includes birds and various feathered dinosaurs. Through these findings, we can gain a better understanding of the evolution of this iconic species.

Leave a Reply