
Nigersaurus is an exciting and unique dinosaur that lived during the middle of the Cretaceous period. It was first discovered in the Sahara Desert of Niger, Africa. It is an herbivore that has an impressive number of 500 teeth, and a unique head shape.
This dinosaur is an important part of the history of the earth and its evolution. It is also an incredible example of how life can survive even in the harshest of environments. This article will provide more information about this remarkable dinosaur and its habits.
Where did Nigersaurus lived?
Nigersaurus lived in present-day Niger, Africa, during the mid-Cretaceous period, about 115 to 97 million years ago. Its remains were first discovered in the Elrhaz Formation of Gadoufaoua in the Sahara Desert.
The fossilized remains of the Nigersaurus were found in an area known as the Ahaggar Mountains, which was once part of a shallow sea. The area is now arid and rocky, but during the mid-Cretaceous period, it was a lush, tropical landscape.
Nigersaurus Diet
Nigersaurus, a genus of long-necked, plant-eating dinosaur that lived some 115 million years ago, had a unique diet that allowed it to survive in its African habitat. The discovery of its remains in Niger in 2000 revealed that Nigerosaurus had a wide-ranging diet.
This included both plant material such as leaves and fruits, and animals such as insects and small amphibians. Nigersaurus had an impressive set of teeth that were suited for a variety of diets. Its teeth were flat and wide, with ridges at the front that helped to strip leaves from plants, and sharp edges that allowed it to cut and chew tough vegetation.
Its wide jaws were also well-suited for a diet of hard-shelled animals like insects. Nigersaurus also had an impressive digestive system that allowed it to break down a variety of food sources. Its stomach contained two chambers, the first of which was used for the rapid breakdown of food, while the second provided a slower, more efficient breakdown.
Nigersaurus’ unique diet was essential for its survival in its African habitat. It allowed it to access a variety of food sources, and its digestive system enabled it to process these sources efficiently. This enabled it to survive in an environment where food sources were scarce.
Nigersaurus Teeth
Recently, paleontologists have discovered a new species of dinosaur related to the Diplodocus, called the Nigersaurus. This species of sauropod lived in what is now Niger in the Middle East about 115 million years ago, during the Early Cretaceous period.
The Nigersaurus was a herbivore, with its long neck and small head, which was similar to the Diplodocus in many ways. However, the most remarkable feature of the Nigersaurus is its teeth. Unlike the hundreds of slender teeth found in other sauropods, the Nigersaurus had only twelve thick, blunt teeth in its mouth.
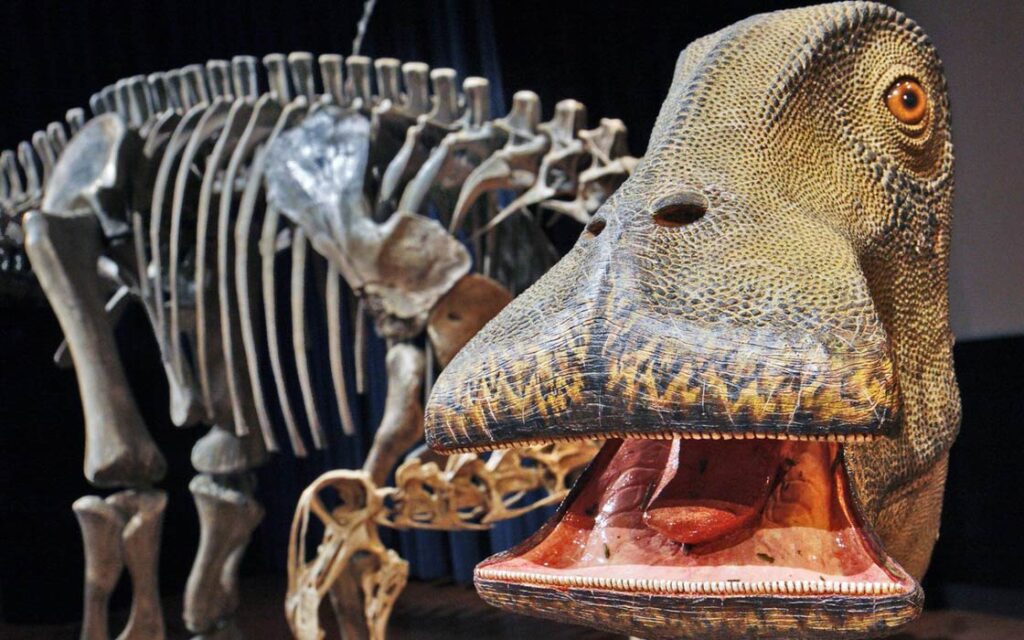
These teeth are like those of a cow, and are likely the result of its different eating habits. While other sauropods may have fed on tough vegetation, the Nigersaurus appears to have been a specialist in eating soft plants.
The teeth of the Nigersaurus are not only unique in shape, but also in their arrangement. The twelve teeth are arranged in a single row on each side of its jaw, which is an unusual feature in sauropods. This arrangement allows the Nigersaurus to effectively cut through its food with a simple jaw movement.
This discovery has shed some light on the feeding habits of sauropods, and it also provides valuable insight into the evolution of plant-eating dinosaurs. The unique tooth structure of the Nigersaurus shows that different types of sauropods may have adapted to different diets in order to survive.
Nigersaurus Weight
The Nigersaurus weighed an estimated 30 tons, making it one of the heaviest sauropod dinosaurs. Its large size has been attributed to its massive ribcage, which contained more air than other sauropods.
This allowed the Nigersaurus to hold in more oxygen, giving it more strength and endurance. Its long neck and small head are thought to have been adapted for grazing on low-lying vegetation, and its wide, flat teeth were likely used for grinding plants.
The Nigersaurus is believed to have lived in the Middle Cretaceous period, some 100 million years ago. Its fossils have been found in Niger, Africa, and its remains are some of the best-preserved sauropod fossils ever discovered.
Facts About Nigersaurus
The Nigersaurus is a species of sauropod dinosaur that lived during the middle of the Cretaceous period in what is now Niger. It is known for its unusually broad, straight-edged muzzle, which was filled with hundreds of teeth. The Nigersaurus is believed to have been a herbivore, living off of a variety of low-lying plants.
The Nigersaurus was first discovered in the early 2000s during an expedition to the Sahara Desert. The fossil remains of the dinosaur were found in an area known as Gadoufaoua, located in Niger. It is believed that the Nigersaurus roamed the area during the mid-Cretaceous period, between 100 and 90 million years ago.
The Nigersaurus is believed to have been around 30 feet long and weighed up to 10 tons. It had a long neck and a wide, flat head. Its muzzle was filled with hundreds of small, conical teeth, which likely served to help the dinosaur graze on a variety of low-lying plants.
The Nigersaurus was an unusual sauropod in that it had a very large number of cervical vertebrae, which gave it its unusual straight-edged muzzle. This feature helped the Nigersaurus to reach a wider variety of plants than most other sauropods.
The Nigersaurus is a remarkable species of dinosaur that helps us to understand more about the ecology of the mid-Cretaceous period. Its unusual morphology and wide muzzle likely allowed it to survive in an environment that would have been difficult for other dinosaur species to thrive in.

Leave a Reply